Dementia is not a single disease, but rather a term that describes a group of symptoms affecting memory, thinking, and social abilities severely enough to interfere with daily functioning.
While memory loss is common, dementia involves much more than just forgetting things.
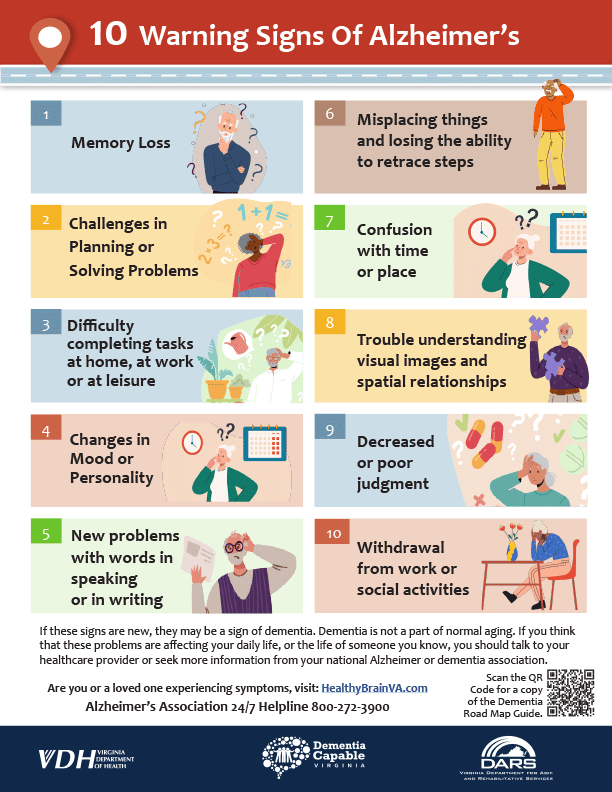
Common Signs and Symptoms
- Memory loss that disrupts daily life
- Difficulty planning or solving problems
- Trouble completing familiar tasks
- Confusion with time or place
- Trouble understanding visual images
- New problems with words in speaking or writing
- Misplacing things and losing the ability to retrace steps
- Decreased or poor judgment
- Withdrawal from work or social activities
- Changes in mood and personality
Normal Aging vs. Dementia
| Normal Aging | Dementia |
|---|---|
| Occasionally forgetting names or appointments | Frequently forgetting recent events or conversations |
| Sometimes having trouble finding the right word | Difficulty with language and communication |
| Making occasional poor decisions | Poor judgment and decision-making abilities |
| Sometimes misplacing things | Putting things in unusual places and being unable to find them |
Types of Dementia
Alzheimer’s Disease
The most common type of dementia, accounting for 60-80% of cases. It’s characterized by the buildup of amyloid plaques and tau tangles in the brain.
- Gradual onset and progression
- Memory loss is often the first symptom
- Affects thinking, behavior, and memory
Lewy Body Dementia
Characterized by abnormal protein deposits called Lewy bodies in the brain.
- Visual hallucinations
- Movement problems similar to Parkinson’s disease
- Fluctuating attention and alertness
Vascular Dementia
Caused by reduced blood flow to the brain, often due to stroke or other blood vessel problems.
- Stepwise progression
- Problems with planning and organization
- May occur alongside Alzheimer’s disease
Frontotemporal Dementia (FTD)
Affects the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain, leading to changes in personality and behavior.
- Changes in personality and behavior
- Difficulty with language
- Often occurs at a younger age (40-65)
For more information about specific diseases, visit:
- Alzheimer’s Association
- Lewy Body Dementia Association
- Association for Frontotemporal Degeneration (AFTD)
- National Institute on Aging
- Alzheimers.gov
Dementia Road Map: A Guide for People Impacted by Dementia

This publication is a stage-by-stage guide to cognitive changes to help guide your journey:
- Information about Alzheimer’s disease and dementia
- Understanding the role of a caregiver (New!)
- What you should expect at each stage
- What you can do at each stage
- Recommended action steps
- Communication tips
- Resources to support you and your loved one
- Information on palliative and hospice care (New!)
This program is managed by Dementia Capable Virginia.